Future Concept MES 4.0
The MES of the future
IT support in production plays a key role for Integrated Industry (in Germany called Industry 4.0). In order to cover future production processes new standards and functions are required, which will especially affect MES applications. With MES 4.0 MPDV introduced a concept for the Manufacturing Execution System (MES) of the future.
Processes can be significantly improved and every day production routines can be tackled more efficiently - also in a decentralized production moving towards Industry 4.0.
MES 4.0 covers the following:
- Interoperability
- Flexibility
- Management support
- Horizontal integration
- Online capability
- Mobility
- Integrative data management
- Decentralization
- Unified Shop Floor Connectivity
- Big Data
- Security by Design
- Human Factor

Other forward-looking MES theories
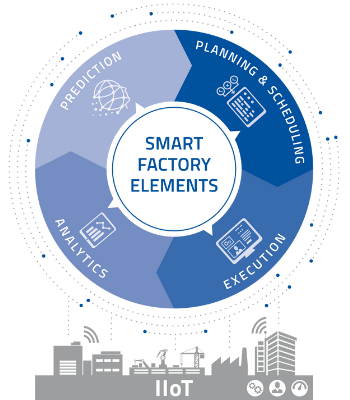
Smart Factory Elements
A model for innovative production IT
The challenges facing production have grown enormously. These challenges are leading to increased complexities like a high product diversity, short delivery times, fast process changes, smaller batch sizes up to batch size 1. In times of Industry 4.0, this is clearly a case for the Smart Factory - which in turn needs certain processes, functions and applications to meet the growing demands. This is a job for the Smart Factory Elements.
The Smart Factory Elements make up a control loop. According to this control loop, production is planned based on specifications from different sources and a plan is then implemented. The data collected is analyzed to make forecasts. Subsequently, the findings from analytics and prediction flow back into planning. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) supports this cycle by collecting and providing data. It also provides real-time applications for the shop floor.
Planning & Scheduling contains typical tasks of the work preparation and planning:
- Orders and operations
- Resources and employees
- Quality assurance
- Maintenance activities
- Material and energy use
Execution ensures that the specifications are implemented and documented efficiently and correctly:
- Production control
- Monitoring process quality
- Process interlocking
- Online monitoring
- Early detection of deviations
Analytics uses statistical methods and innovative algorithms to prepare collected data for:
- KPIs Performance and correlation analysis
- Root Cause Analysis
- Self service analytics
- Machine learning based on Big Data
Prediction enables the prediction of events based on executable models and artificial intelligence.
Typical applications are:
- Predictive quality
- Prediction of dates
- Predictive Maintenance
- Projection of material ranges
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) connects the operator and the real world of production with the digital image of the Smart Factory by means of networking and edge computing.
The following applications are used:
- Data transfer from IIoT sensors D
- igital machine connections
- Manual data collection
- Providing information to the shop floor
- Flexible operator guidance