Find out how you can digitalize your production
with solutions from MPDV!
Value Stream – Smart Factory Glossary
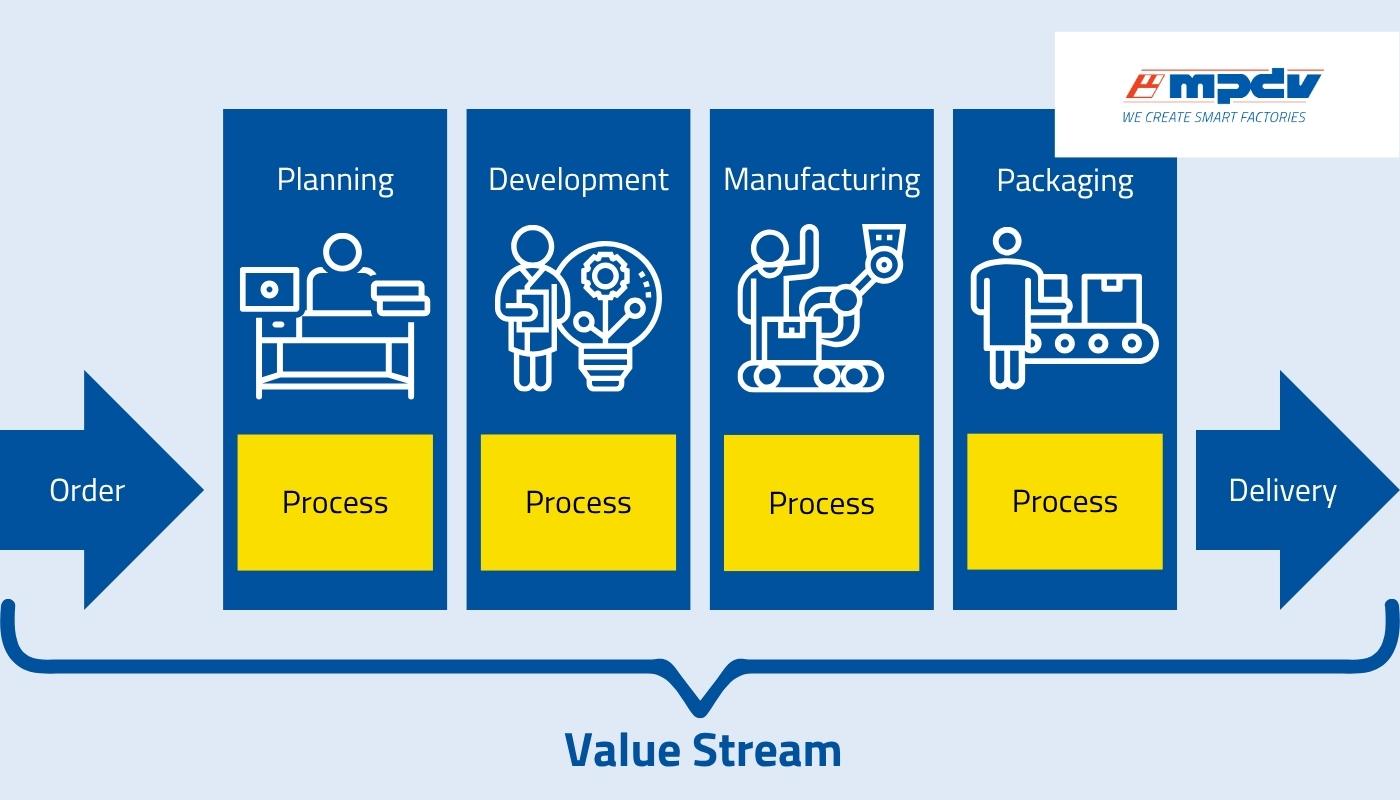
A value stream covers all actions and processes necessary to manufacture a product or offer a service — from raw material to finished product. The concept is used in particular in production planning and control where it is essential to avoid waste of all kind. The value stream, its analysis and optimization, is a key element of lean management.
The value of a product is starting point and basis of any value stream. A product's value is determined by what the customer is willing to pay for it. With focus on the actual product value, a value stream is created: This stream includes all activities from development and design of the product to order and manufacturing up to shipping. The value stream is not only about material flows, but also integrates information flows. As only the object value is of interest, other things such as departmental boundaries are ignored. The approach is holistic as the aim is to achieve the lowest possible product or service costs across all departments and processes.
The value stream considers different types of activities:
- Value-adding activities: These activities contribute directly to creating a product or service and generate value.
- Necessary non-value-adding activities: These activities do not add any value, but are still required. Examples are wait times in production or service times.
- Unnecessary non-value-adding activities: These activities do not add any value and are not essential. They are also known as waste.
Value stream mapping for lean value streams
A value stream mapping helps to identify inefficiencies – for example unnecessary non-value-adding activities – and to optimize the overall process. A value stream map visualizes the results of the value stream mapping and shows the entire value stream in a diagram. Not only value-adding activities such as assembly or processing are mapped in this diagram, but also different types of waste, for example overproduction, waiting times, or transport.
Once the weak points are identified, a value stream design showing the intended optimizations can be created. It aims at reducing waste and shortening the time from order to delivery while changing production according to customer requirements and improving on-time delivery and reliability. Lean value streams are one of the four building blocks on the way to a perfect production. To support companies on their journey to perfect production and manufacturing excellence, MPDV's Executive Manufacturing Center (EMC) offers comprehensive consulting services.
Material and information flows in the value stream
The typical value stream of a manufacturing company includes material and information flows. When you start visualizing these flows in a value stream map, the manufacturing process and the material flow are first set up, followed by the information flows and planning processes.
Material flow
- Procurement and storage of raw materials
- Transport within production
- Processing, assembly, and inspection processes
- Temporary storage and buffer stocks
- Packaging and shipping of the finished product
Information flow
- Acceptance and control of orders (e.g. with an ERP system)
- Production planning and control (e.g. with an Advanced Planning and Scheduling System)
- Communication between departments (e.g., production planning, purchasing, logistics)
- Feedback from production (e.g. quality inspections, progress reports)
Sources
- Value stream: Wikipedia, 26.09.2024 [online] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Value_stream (requested 13.03.2025).
Would you like more information? We are happy to help.
Just fill in the form below. We will take care of your inquiry promptly.